Extracellular vesicles isolation by membrane binding peptide modified beads
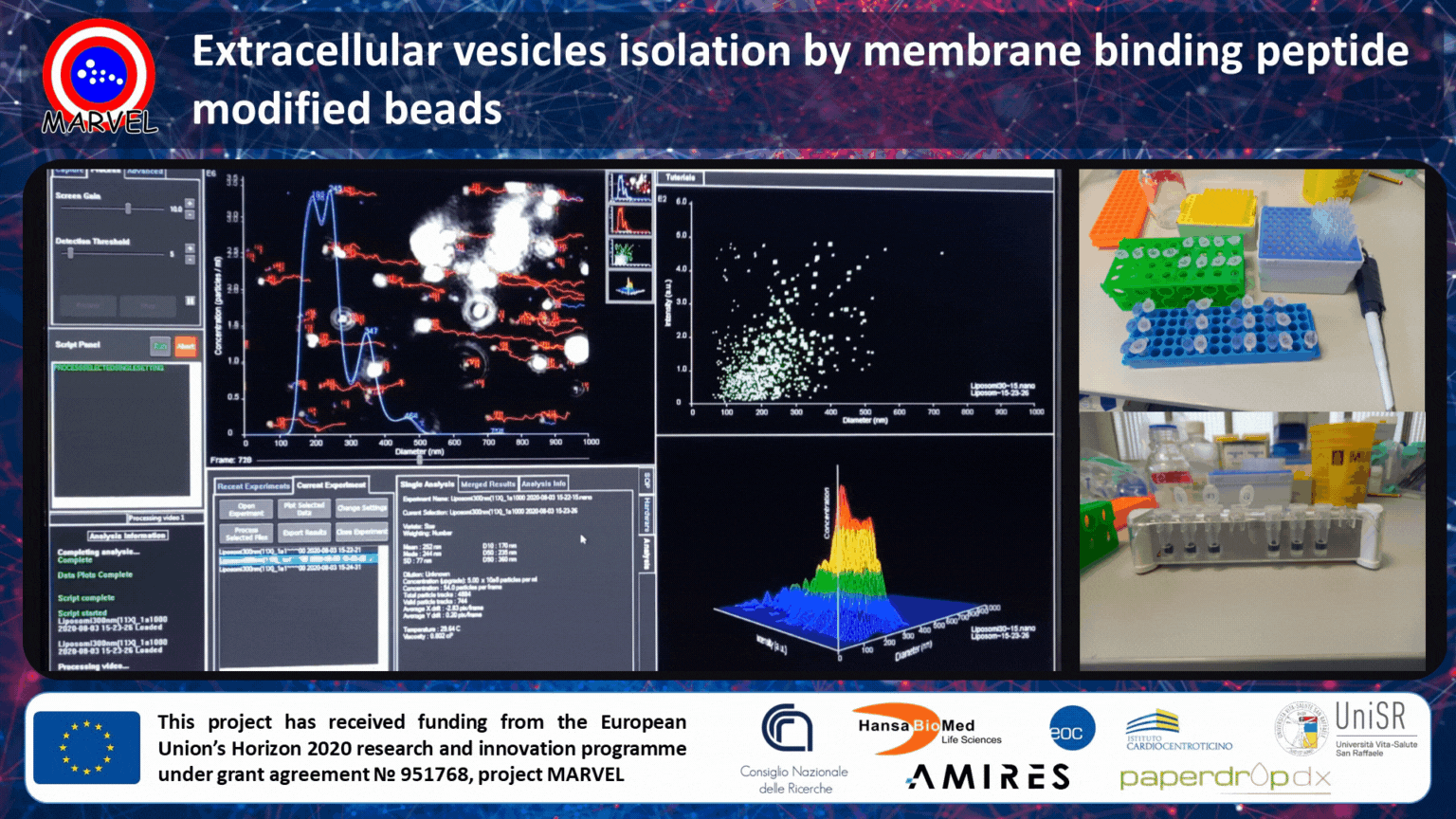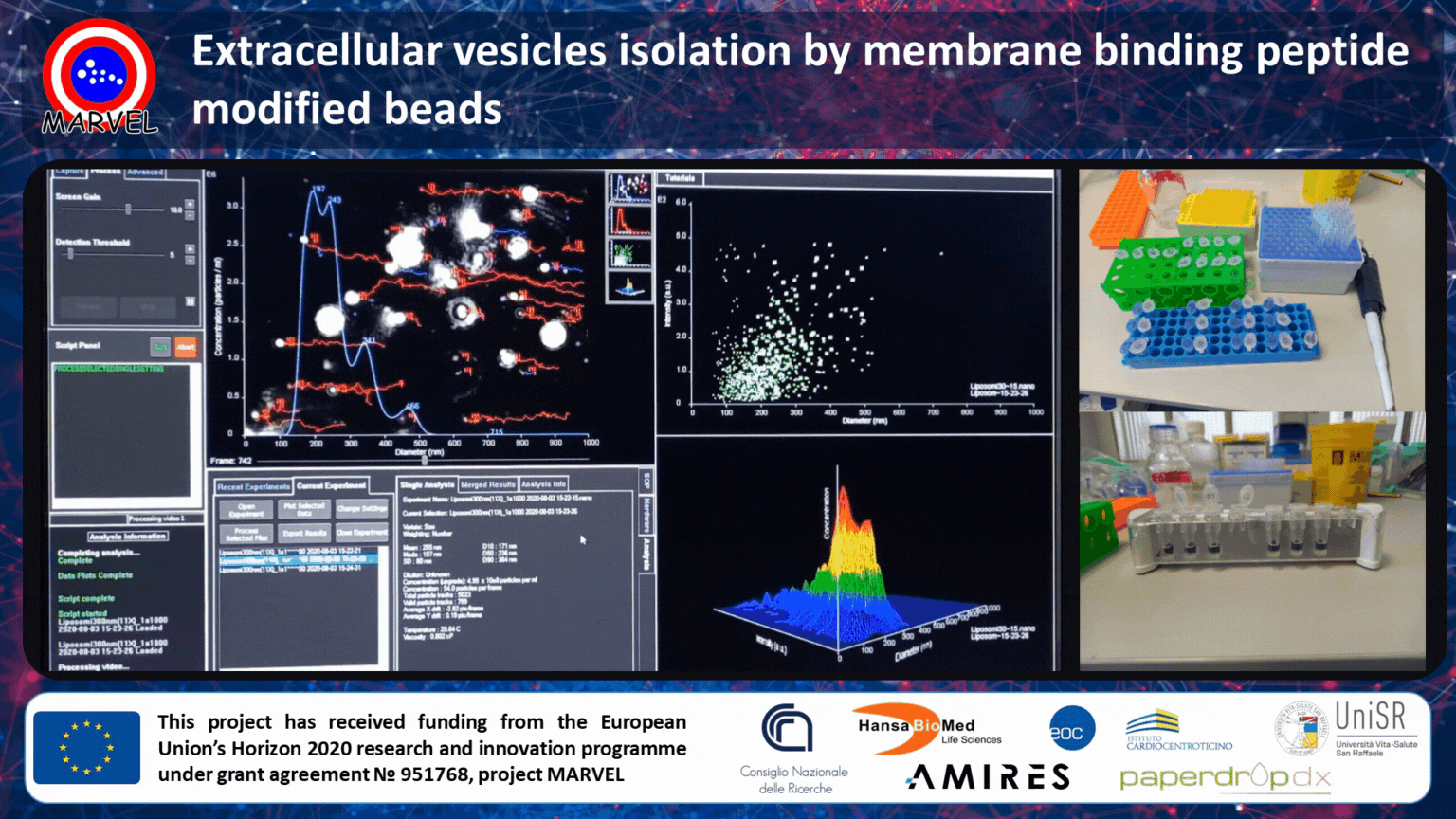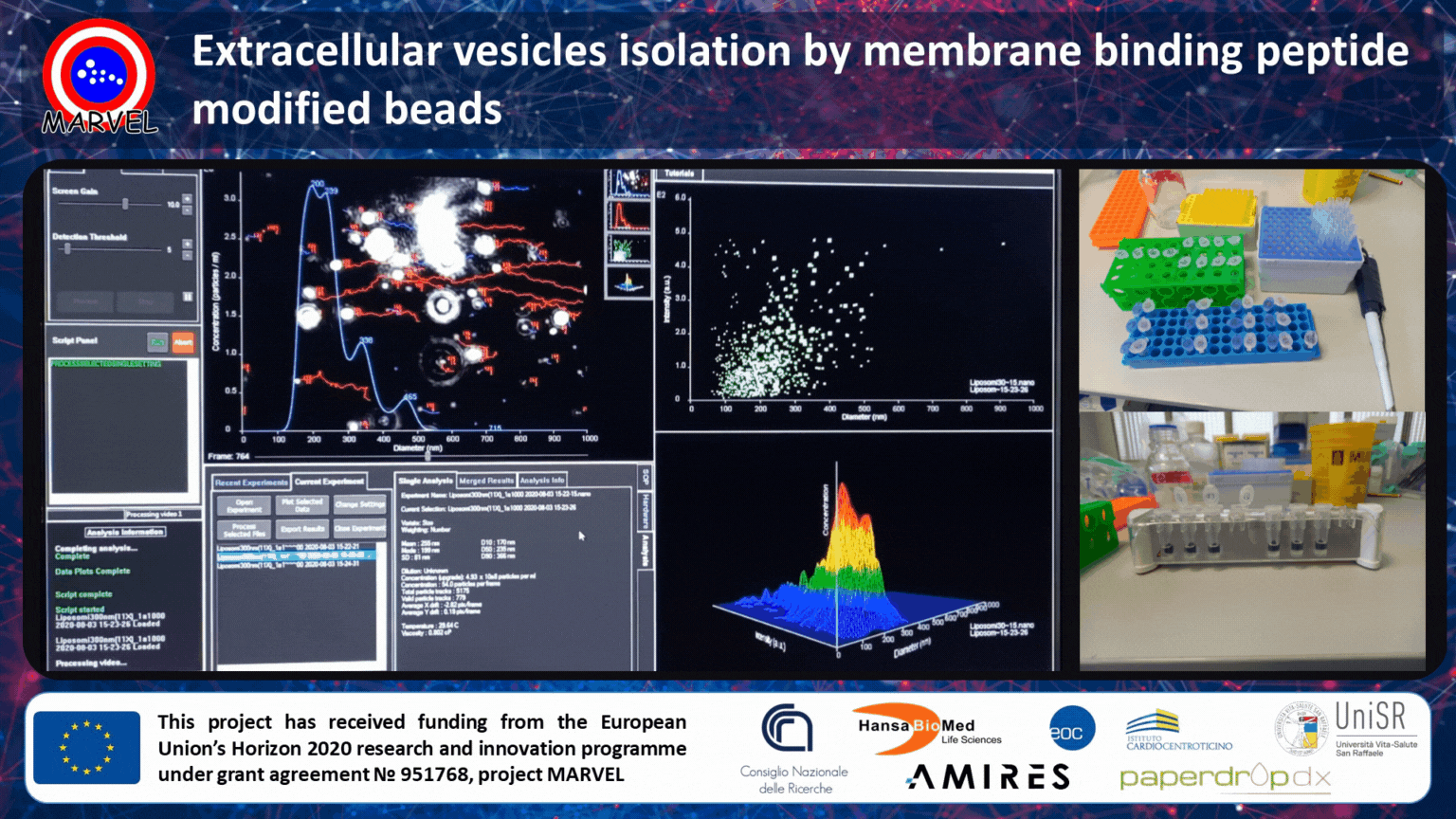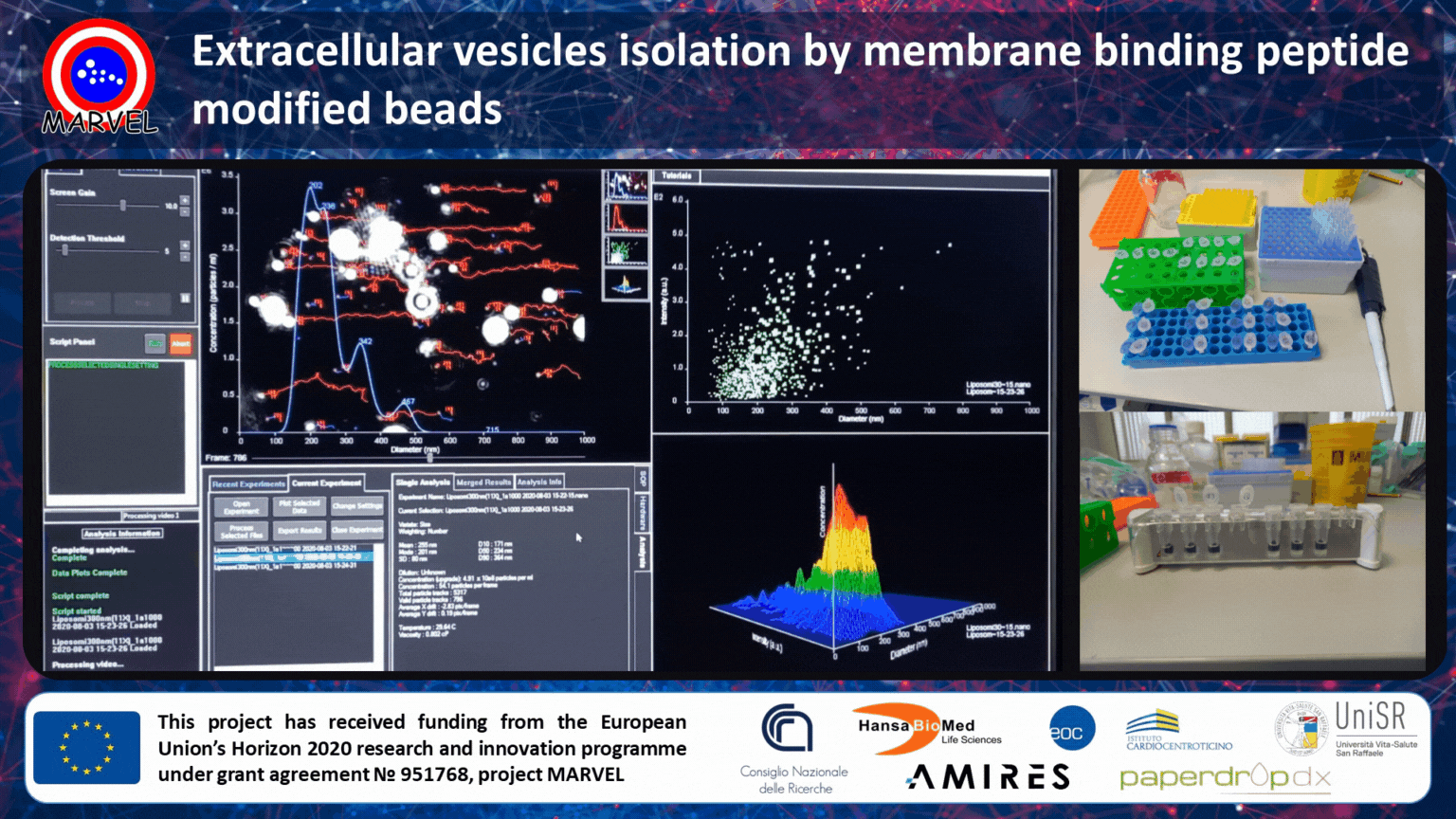
MARVEL project partner, CNR-SCITEC, is currently working on the optimization and validation of membrane-binding peptide-modified beads for unbiased (universal) and scalable isolation of extracellular vesicles (EVs) from different kinds of biological fluids (plasma, urine, serum, etc.).
Extracellular vesicles are secreted by cells into the extracellular space and they are implicated in a wide range of physiological processes and diseases. This has led to an explosion of interest in using EVs in a variety of tissue engineering applications. For example, EVs have great potential to be used as markers for disease initiation, progression, and response to treatment, as well as hold huge potential as mediators of tissue regeneration. Nowadays, the main drawback of antibody-based affinity isolation by beads is the low scalability and underrepresented isolation (only sub-populations are isolated).
In MARVEL, we are developing a bead-based affinity isolation system by using a universal, yet highly specific, interaction with membrane sensing peptides. This allows scalable capturing of all small EVs unbiased by the differential expression of surface markers. The MARVEL technology outperforms tetraspanin antibody capturing and ensures high recovery and exquisite specificity against common contaminants. Currently, we are validating our technology in cell culture supernatants, serum/plasma, and urine.